The problems of speech separation and enhancement concern the extraction of the speech emitted by a target speaker when placed in a scenario where multiple interfering speakers or noise are present, respectively. A plethora of practical applications such as home assistants and teleconferencing require some sort of speech separation and enhancement preprocessing before applying Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems. In the recent years, most techniques have focused on the application of deep learning to either time-frequency or time-domain representations of the input audio signals. In this paper we propose a real-time multichannel speech separation and enhancement technique, which is based on the combination of a directional representation of the soundfield, denoted as beamspace, with a lightweight Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). We consider the case where the Direction-of-Arrival (DOA) of the target speaker is approximately known, a scenario where the power of the beamspace-based representation can be fully exploited, while we make no assumption regarding the identity of the talker. We present experiments where the model is trained on simulated data and tested on real recordings and we compare the proposed method with a similar state-of-the-art technique.
Method
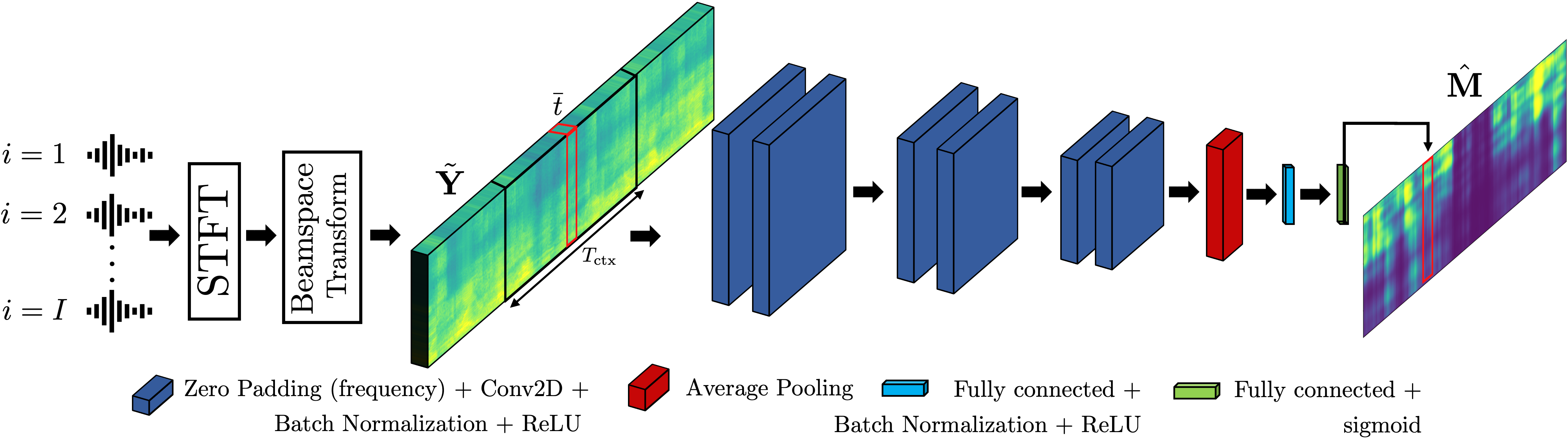
Listening tests
Here below we report some audio examples along with the spectrogram of the signals.
For each example the setup with the numner of interferers R, the mixture at the first microhone and the desired target are depicted.
We compare the results of the proposed method with the NBDF approach and the mixture beamformer steered to 90°.
For each setup we report the comparison between the three array configuration used in the validation. Hence, I=4 with d=26mm, and I=3, I=4 with d=52mm.
| EXAMPLE 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Setup SOI=1 R=2 |

|

|

|
|
I = 4 d = 26mm |
 SDR=-3.24dB
SDR=-3.24dB
|
 SDR=-0.86dB
SDR=-0.86dB
|
 SDR=-0.23dB
SDR=-0.23dB
|
|
I = 3 d = 52mm |
 SDR=0.74dB
SDR=0.74dB
|
 SDR=3.64dB
SDR=3.64dB
|
 SDR=4.05dB
SDR=4.05dB
|
|
I = 4 d = 52mm |
 SDR=1.08dB
SDR=1.08dB
|
 SDR=0.29dB
SDR=0.29dB
|
 SDR=1.1dB
SDR=1.1dB
|
| EXAMPLE 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Setup SOI=1 R=3 |

|

|

|
|
I = 4 d = 26mm |
 SDR=3.64dB
SDR=3.64dB
|
 SDR=0.23dB
SDR=0.23dB
|
 SDR=4.51dB
SDR=4.51dB
|
|
I = 3 d = 52mm |
 SDR=3.77dB
SDR=3.77dB
|
 SDR=2.92dB
SDR=2.92dB
|
 SDR=8.08dB
SDR=8.08dB
|
|
I = 4 d = 52mm |
 SDR=3.55dB
SDR=3.55dB
|
 SDR=1.09dB
SDR=1.09dB
|
 SDR=4.42dB
SDR=4.42dB
|
| EXAMPLE 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Setup SOI=1 R=0 |

|

|

|
|
I = 4 d = 26mm |
 R_soi= -
R_soi= -
|
 R_soi=-1.86db
R_soi=-1.86db
|
 R_soi=-5.53db
R_soi=-5.53db
|
|
I = 3 d = 52mm |
 R_soi= -
R_soi= -
|
 R_soi=-0.5db
R_soi=-0.5db
|
 R_soi=-2.48db
R_soi=-2.48db
|
|
I = 4 d = 52mm |
 R_soi= -
R_soi= -
|
 R_soi=-0.06db
R_soi=-0.06db
|
 R_soi=-5.54db
R_soi=-5.54db
|
| EXAMPLE 4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Setup SOI=1 R=1 |

|

|

|
|
I = 4 d = 26mm |
 SDR=4.87dB
SDR=4.87dB
|
 SDR=1.84dB
SDR=1.84dB
|
 SDR=2.06dB
SDR=2.06dB
|
|
I = 3 d = 52mm |
 SDR=4.58dB
SDR=4.58dB
|
 SDR=5.06dB
SDR=5.06dB
|
 SDR=5.14dB
SDR=5.14dB
|
|
I = 4 d = 52mm |
 SDR=5.05dB
SDR=5.05dB
|
 SDR=1.33dB
SDR=1.33dB
|
 SDR=3.87dB
SDR=3.87dB
|
| EXAMPLE 5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Setup SOI=0 R=4 |

|

|

|
|
I = 4 d = 26mm |
 R_interf= -
R_interf= -
|
 R_interf=-7.88dB
R_interf=-7.88dB
|
 R_interf=-13.98dB
R_interf=-13.98dB
|
|
I = 3 d = 52mm |
 R_interf= -
R_interf= -
|
 R_interf=-12.04dB
R_interf=-12.04dB
|
 R_interf=-12.59dB
R_interf=-12.59dB
|
|
I = 4 d = 52mm |
 R_interf= -
R_interf= -
|
 R_interf=-13.46dB
R_interf=-13.46dB
|
 R_interf=-13.68dB
R_interf=-13.68dB
|
| EXAMPLE 6 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Setup SOI=0 R=3 |

|

|

|
|
I = 4 d = 26mm |
 R_interf= -
R_interf= -
|
 R_interf=-38.16dB
R_interf=-38.16dB
|
 R_interf=-43.03dB
R_interf=-43.03dB
|
|
I = 3 d = 52mm |
 R_interf= -
R_interf= -
|
 R_interf=-24.94dB
R_interf=-24.94dB
|
 R_interf=-17.58dB
R_interf=-17.58dB
|
|
I = 4 d = 52mm |
 R_interf= -
R_interf= -
|
 R_interf=-27.78dB
R_interf=-27.78dB
|
 R_interf=-22.11dB
R_interf=-22.11dB
|